Add Something, If You'd 👍
Add something, if you'd 👍

Pedro Bertolini
More Posts from Styles987 and Others
Stellar Winds
Stellar winds are fast moving flows of material (protons, electrons and atoms of heavier metals) that are ejected from stars. These winds are characterised by a continuous outflow of material moving at speeds anywhere between 20 and 2,000 km/s.
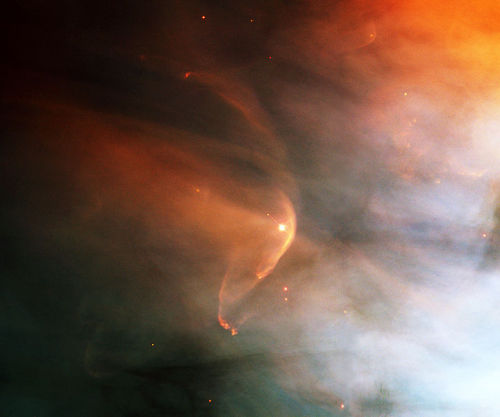

In the case of the Sun, the wind ‘blows’ at a speed of 200 to 300 km/s from quiet regions, and 700 km/s from coronal holes and active regions.
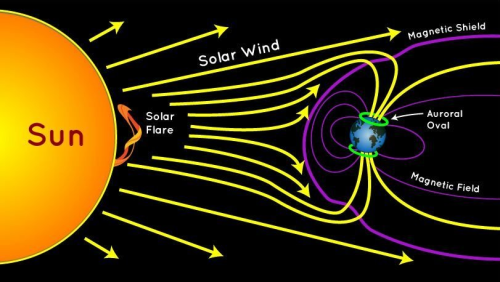
The causes, ejection rates and speeds of stellar winds vary with the mass of the star. In relatively cool, low-mass stars such as the Sun, the wind is caused by the extremely high temperature (millions of degrees Kelvin) of the corona.

his high temperature is thought to be the result of interactions between magnetic fields at the star’s surface, and gives the coronal gas sufficient energy to escape the gravitational attraction of the star as a wind. Stars of this type eject only a tiny fraction of their mass per year as a stellar wind (for example, only 1 part in 1014 of the Sun’s mass is ejected in this way each year), but this still represents losses of millions of tonnes of material each second. Even over their entire lifetime, stars like our Sun lose only a tiny fraction of 1% of their mass through stellar winds.
In contrast, hot, massive stars can produce stellar winds a billion times stronger than those of low-mass stars. Over their short lifetimes, they can eject many solar masses (perhaps up to 50% of their initial mass) of material in the form of 2,000 km/sec winds.

These stellar winds are driven directly by the radiation pressure from photons escaping the star. In some cases, high-mass stars can eject virtually all of their outer envelopes in winds. The result is a Wolf-Rayet star.
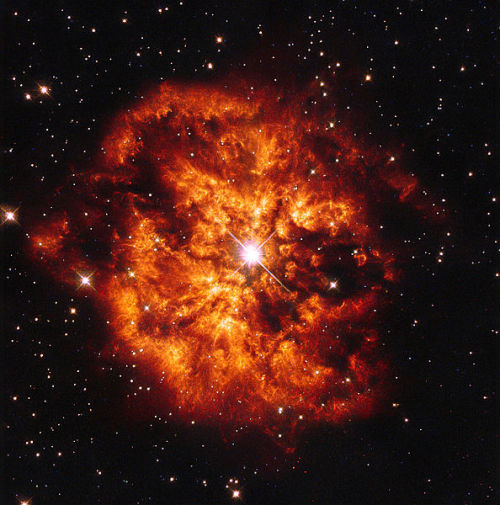

Stellar winds play an important part in the chemical evolution of the Universe, as they carry dust and metals back into the interstellar medium where they will be incorporated into the next generation of stars.
source (read more) + Wolf–Rayet star
Build your own game by clicking today's #GoogleDoodle celebrating the pioneer of the video game cartridge: Jerry Lawson! https://g.co/doodle/pqvgtc3

Look at this... 👀
Look at this GIF... 👀 https://pin.it/1QkYXr5
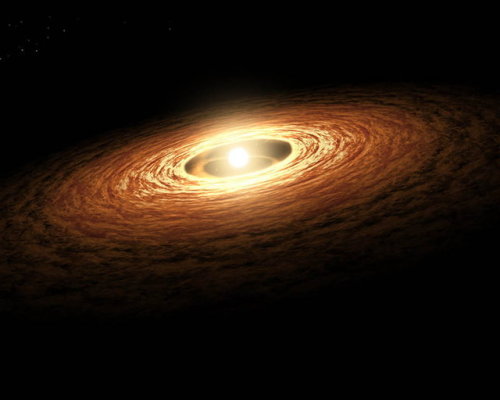
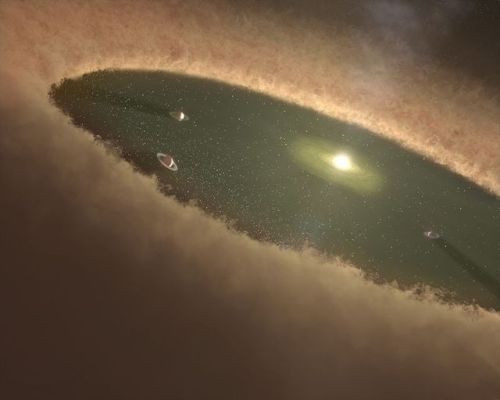








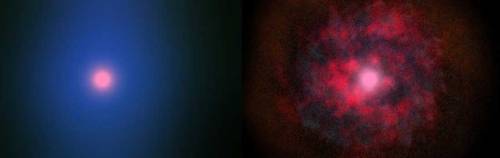
A protoplanetary disk is a rotating circumstellar disk of dense gas and dust surrounding a young newly formed star, a T Tauri star, or Herbig Ae/Be star. The protoplanetary disk may also be considered an accretion disk for the star itself, because gases or other material may be falling from the inner edge of the disk onto the surface of the star. This process should not be confused with the accretion process thought to build up the planets themselves. Externally illuminated photo-evaporating protoplanetary disks are called proplyds.
The nebular hypothesis of solar system formation describes how protoplanetary disks are thought to evolve into planetary systems. Electrostatic and gravitational interactions may cause the dust and ice grains in the disk to accrete into planetesimals. This process competes against the stellar wind, which drives the gas out of the system, and gravity (accretion), which pulls material into the central T Tauri star.
source
Image credit: NASA/JPL, ESO
Look at this... 👀
Look at this... 👀 https://pin.it/15yw4oy

-
 imgaydude94 liked this · 6 days ago
imgaydude94 liked this · 6 days ago -
 cunningsilencestranger liked this · 1 week ago
cunningsilencestranger liked this · 1 week ago -
 captiangarth liked this · 1 week ago
captiangarth liked this · 1 week ago -
 gaysex1424 liked this · 1 week ago
gaysex1424 liked this · 1 week ago -
 fuckbuddygayboy66 liked this · 1 week ago
fuckbuddygayboy66 liked this · 1 week ago -
 datwinz09 reblogged this · 1 week ago
datwinz09 reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 datwinz09 liked this · 1 week ago
datwinz09 liked this · 1 week ago -
 zadrian liked this · 1 week ago
zadrian liked this · 1 week ago -
 iluvanor liked this · 1 week ago
iluvanor liked this · 1 week ago -
 kaiserwjk liked this · 1 week ago
kaiserwjk liked this · 1 week ago -
 4pp4loos4 liked this · 1 week ago
4pp4loos4 liked this · 1 week ago -
 a-furioussoulcollection-fan liked this · 1 week ago
a-furioussoulcollection-fan liked this · 1 week ago -
 funallthetime69 liked this · 1 week ago
funallthetime69 liked this · 1 week ago -
 holycollectorsublime liked this · 1 week ago
holycollectorsublime liked this · 1 week ago -
 hockeystud62-9 liked this · 1 week ago
hockeystud62-9 liked this · 1 week ago -
 minshnsho liked this · 1 week ago
minshnsho liked this · 1 week ago -
 flyingregulatoragain reblogged this · 1 week ago
flyingregulatoragain reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 flyingregulatoragain liked this · 1 week ago
flyingregulatoragain liked this · 1 week ago -
 downhillrunsblog liked this · 1 week ago
downhillrunsblog liked this · 1 week ago -
 hofe1952 liked this · 1 week ago
hofe1952 liked this · 1 week ago -
 gordon222xe liked this · 1 week ago
gordon222xe liked this · 1 week ago -
 uraeuseraph liked this · 1 week ago
uraeuseraph liked this · 1 week ago -
 rod847566 liked this · 1 week ago
rod847566 liked this · 1 week ago -
 pascartes6 reblogged this · 1 week ago
pascartes6 reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 pascartes6 liked this · 1 week ago
pascartes6 liked this · 1 week ago -
 johnplay liked this · 1 week ago
johnplay liked this · 1 week ago -
 macbumm liked this · 1 week ago
macbumm liked this · 1 week ago -
 mirkos-posts liked this · 1 week ago
mirkos-posts liked this · 1 week ago -
 lovely-demons reblogged this · 1 week ago
lovely-demons reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 jaboticasworld liked this · 1 week ago
jaboticasworld liked this · 1 week ago -
 adamska07 liked this · 1 week ago
adamska07 liked this · 1 week ago -
 tmj469bc liked this · 1 week ago
tmj469bc liked this · 1 week ago -
 conformalcucumber liked this · 1 week ago
conformalcucumber liked this · 1 week ago -
 patrykdapu liked this · 1 week ago
patrykdapu liked this · 1 week ago -
 aguywithoutareason liked this · 1 week ago
aguywithoutareason liked this · 1 week ago -
 edgarwhitmanwilde reblogged this · 1 week ago
edgarwhitmanwilde reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 edgarwhitmanwilde liked this · 1 week ago
edgarwhitmanwilde liked this · 1 week ago -
 sweatyinfluenceryouth liked this · 1 week ago
sweatyinfluenceryouth liked this · 1 week ago -
 lostcauseuk reblogged this · 1 week ago
lostcauseuk reblogged this · 1 week ago -
 lostcauseuk liked this · 1 week ago
lostcauseuk liked this · 1 week ago -
 jessexyron liked this · 1 week ago
jessexyron liked this · 1 week ago -
 ya-ron liked this · 1 week ago
ya-ron liked this · 1 week ago -
 niceplacetostop liked this · 1 week ago
niceplacetostop liked this · 1 week ago -
 seimsamsaramort liked this · 1 week ago
seimsamsaramort liked this · 1 week ago

